 English
English Français
Français
Control techniques for Autonomic Smart Environments
Context
This project grouped members from Inria, LIG, Gipsa-lab and CEA LETI/DACLE and concerned the general topic of Control techniques for Autonomic Smart Environments, with a special emphasis on relating discrete and stochastic control models with middleware platforms applied to smart environments. It enabled us to hire two Masters students for 2016.
Obtained scientific results
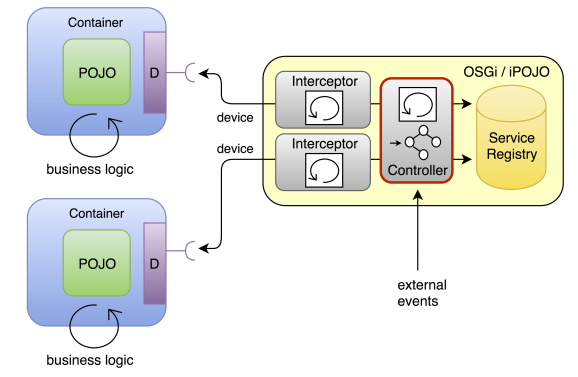
A service-oriented approach to smart home applications control with reactive programming
This work constituted the M2R internship of Armando Ochoa, and was performed in cooperation with the Adele team at LIG, co-advised by E. Rutten and V. Lestideau. The need for adaptability in pervasive computing is growing, driven in part by the increasing number and variety of communication devices. In autonomic applications, however, the control architecture frequently becomes itself a complex system that needs to be adapted. Autonomic applications are often composed of multiple control loops? each addressing a specific aspect ? whose execution needs to be coordinated for efficient and correct administration. We therefore propose to investigate the use of reactive control models with events and states to coordinate autonomic loops in service-oriented architectures. In this work, we illustrate our approach by integrating a controller based on discrete controller synthesis in an autonomic pervasive environment. The role of the controller is to influence the service-binding criteria of multiple control loops, while respecting logical constraints. In particular, we consider reconfiguration operations of known and dynamic service sets.
Multi Objective Optimal Reconfiguration of a Smart Home Platform
This work constituted the M2R internship of Ronak Feizimirkhani, co-advised by S. Mocanu and V. Lestideau. The context is the development of an application for a smart home in which automation devices are connected through a wireless communication protocol, Z-Wave, and controlled by a central controller, USB plug in. This involves methods and tools to design fail-safe controllers for autonomic, adaptive, reconfigurable computing systems by combining Computer Science and Control Theory techniques. For this purpose, it is necessary to access required information over the network, derive out a simplified model of the physical network, and then link it to the User interface application. According to the information achieved, there will be an estimation of the network diagnostics to find some probable solutions for. The final application is in a user media to do installing, maintaining or even optimizing the network and devices.
Publications
- Armando Ochoa. A service-oriented approach to smart home applications control with reactive programming. Master's Thesis, UGA, Grenoble, France, 2016.
- Ronak Feizimirkhani. Multi Objective Optimal Reconfiguration of a Smart Home Platform. Master's Thesis, UGA, Grenoble, France, 2016.


 Sign in
Sign in